Last month we summarised the systematic review by Jayedi A et al. The review concluded that for people with type 2 diabetes every 30 min/week of supervised moderate to vigorous intensity aerobic exercise training significantly reduced HbA1c, with the greatest reduction seen with 100 min/week, compared to no intervention or usual activity. The certainty of the evidence was rated strong.
Some findings are included in this infographic.
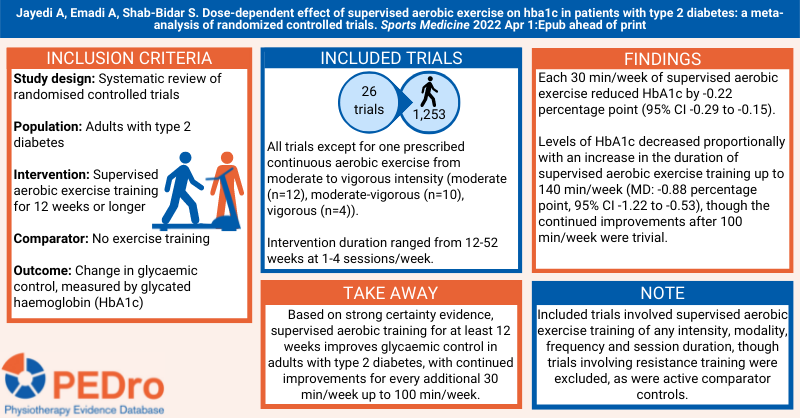
Jayedi A, Emadi A, Shab-Bidar S. Dose-dependent effect of supervised aerobic exercise on hba1c in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sports Medicine 2022 Apr 1:Epub ahead of print https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-022-01673-4



